Wood Cutting Techniques; What is the Best for Timber Flooring?
When it comes to creating luxury hardwood floors, the method of cutting timber plays a crucial role in determining the final appearance, durability, and performance of the flooring. There are several primary methods for cutting timber, each with its own advantages and drawbacks. In this article, we will explore the most common techniques used in the timber flooring industry: quarter sawn, rift sawn, plain sawn (also known as live sawn), and end grain. We’ll discuss each method in detail and outline their specific pros and cons, helping you make an informed choice for your next timber flooring project.
Plain Sawn (Live Sawn) Timber
Description: Plain sawn, also known as live sawn, is the most common and efficient method of cutting timber. The log is cut tangentially to the growth rings, resulting in a wide variety of grain patterns, including cathedral peaks and loops.
Pros:
- Efficient and Cost-Effective: This method maximizes the yield from each log, making it more affordable.
- Varied Grain Patterns: The diverse grain patterns can add a unique and dynamic aesthetic to flooring.
Cons:
- Tendency to Warp: Plain sawn boards are more prone to warping and cupping due to the way the grain is exposed.
- Less Stable: Compared to other methods, plain sawn timber can be less dimensionally stable, especially in environments with fluctuating humidity.
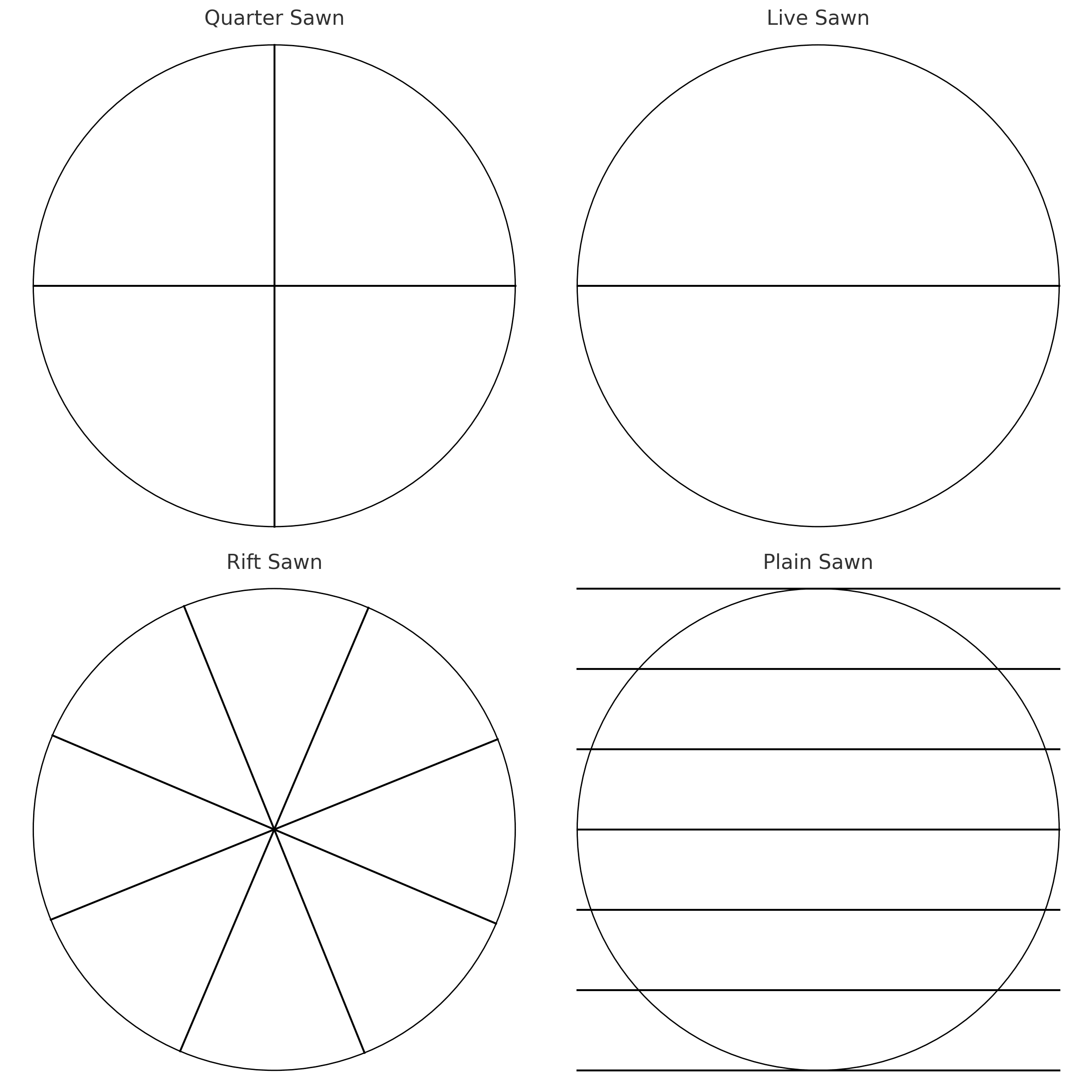
Quarter Sawn Timber
Description: Quarter sawn timber is produced by first cutting the log into quarters and then sawing perpendicular to the growth rings. This method creates a linear grain pattern that is more uniform and less pronounced than plain sawn timber.
Pros:
- Increased Stability: Quarter sawn boards are less likely to warp, cup, or twist, making them ideal for environments with varying moisture levels.
- Aesthetic Appeal: The linear grain pattern is often considered more refined and attractive, and it can feature unique ray flecks, especially in species like oak.
- Wear Resistance: The vertical grain structure provides greater resistance to wear and tear, making it suitable for high-traffic areas.
Cons:
- Higher Cost: The process yields less usable timber and is more labor-intensive, leading to higher costs.
- Limited Availability: Due to its lower yield and higher demand, quarter sawn timber can be harder to source.
Rift Sawn Timber
Description: Rift sawn timber is cut at a slight angle to the radial, typically between 30° to 60°, resulting in a tight, straight grain pattern. This method is less common and more expensive due to its lower yield.
Pros:
- Superior Stability: Like quarter sawn timber, rift sawn boards offer excellent dimensional stability and are less prone to movement.
- Consistent Grain: The straight grain pattern is highly uniform and considered very desirable for a sleek, modern look.
- Minimal Seasonal Gapping: This method minimizes the gaps that can occur between boards during seasonal changes.
Cons:
- Expensive: The lower yield and more complex sawing process make rift sawn timber the most expensive option.
- Wasteful: This method produces more waste compared to plain sawn and quarter sawn techniques.
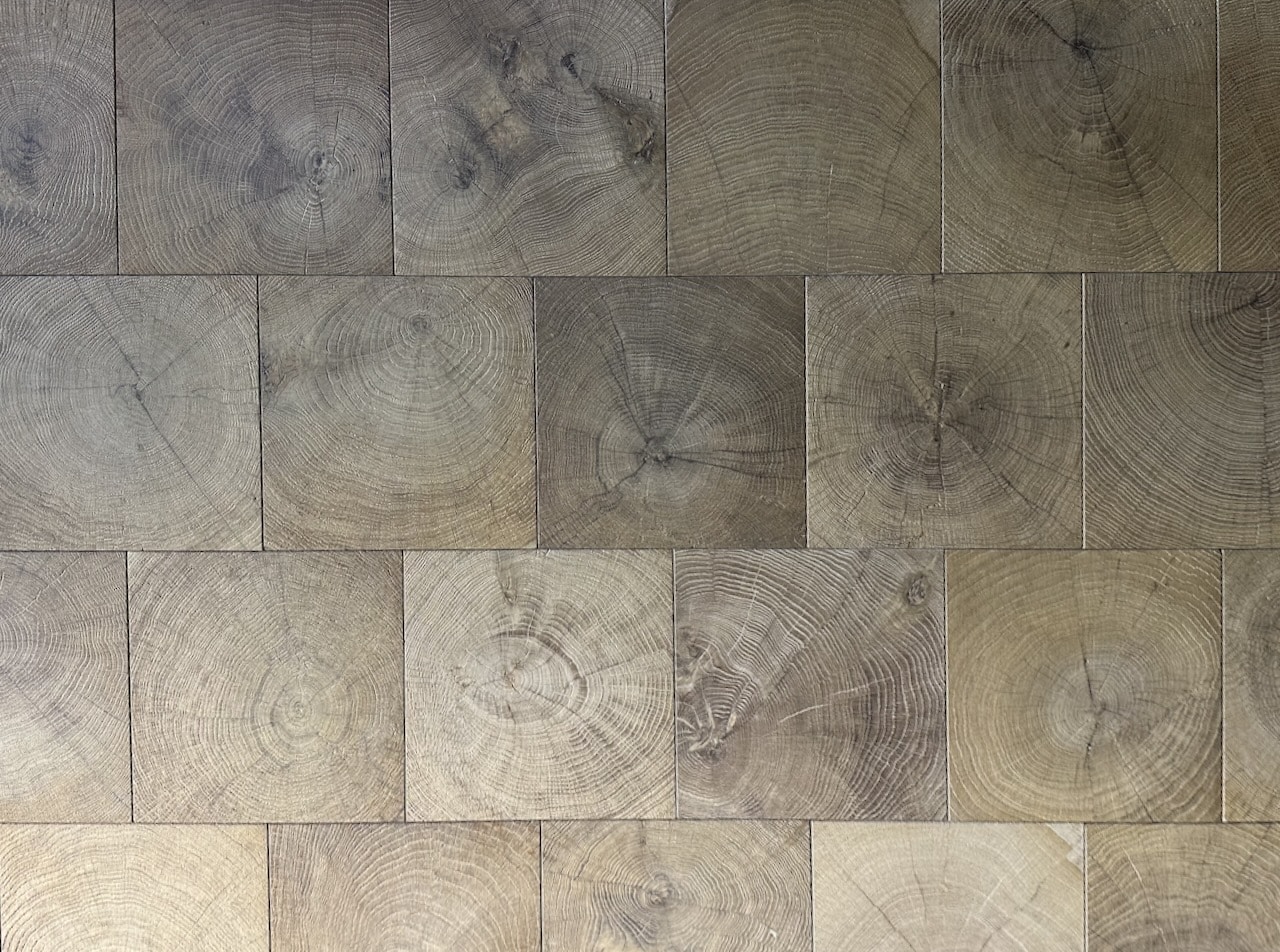
End Grain Timber
Description: End grain timber is created by cutting the log cross-sectionally, exposing the ends of the growth rings. This method is often used for specialty flooring and creates a unique, block-like pattern.
Pros:
- Exceptional Durability: End grain boards are extremely hard and wear-resistant, ideal for high-impact areas.
- Unique Appearance: The pattern created by end grain cutting is distinctive and can add a bold statement to any space.
- Natural Resilience: The orientation of the grain makes end grain timber naturally resistant to splitting and chipping.
Cons:
- Complex Installation: End grain flooring can be more challenging to install and requires a skilled professional.
- High Cost: The intricate cutting and installation process make end grain timber one of the more expensive options.

For more information on timber flooring and expert advice on choosing the right type of wood for your project, feel free to contact us at Vienna Woods, your Auckland wood flooring specialist. Whether you’re looking for luxury hardwood floors or specialist wood flooring solutions, we are here to help you every step of the way.



